4e BC
Beginning of animal testing in ancient Greece.

1780
Jeremy Bentham argued for better treatment of animals on the basis of their ability to feel pleasure and pain, famously writing, "The question is not, Can they reason? nor, Can they talk? but, Can they suffer?"

1981
OECD creates MAD (Mutual acceptance of data) to reduces duplicative testing, allows governments to work together when assessing chemicals, and saves government and industry resources

2004
On 11th September 2004 the ban on animal tested cosmetic products came into force. The sale of cosmetic ingredients tested on animals outside the EU using methods that have been replaced within the EU was also banned.

2010
Directive 2010/63/EU is the European Union (EU) legislation "on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes" and is one of the most stringent ethical and welfare standards worldwide.

1493
Birth of Paracelsus, the Father of Toxicology
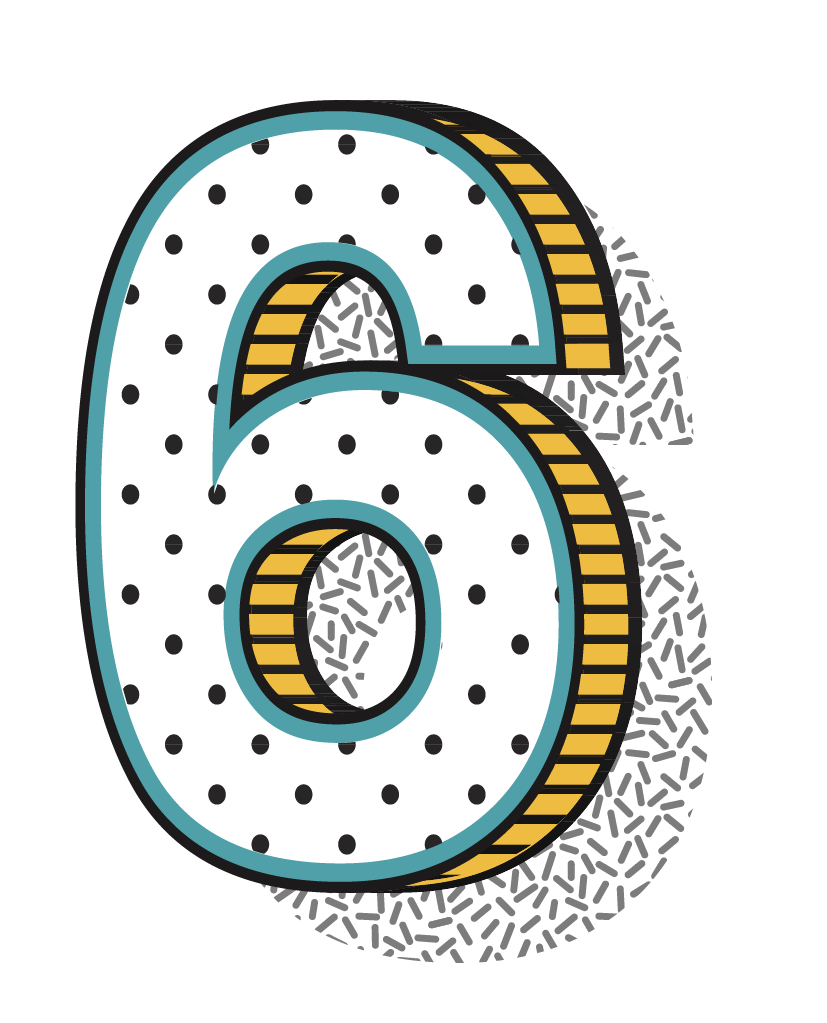

1824
Creation of the first Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals.

1959
Russell & Burch publish “ The Principles of of Humane Experimental Technique”, a book that sets out the philosophy of the 3Rs; Refinement, Reduction and Replacement, regarding the use of animals in scientific experiments.

2004
“The triples” The first in vitro OECD test guidelines are published ! TG 430-431-432 on skin corrosion and phototoxicity!

2010
Consecutively to the application of Directive 2010/63/EU, dissections are banned in all secondary schools.

2012
Lush prize in founded. It is a unique collaboration between Lush Cosmetics and Ethical Consumer Research Association.

1532
“wisdom enters not into a malicious mind, and science without conscience is but the ruin of the soul” Rabelais, Pantagruel - Rabelais sets with this idea the basis of bioethic, trying to reconcile scientific capability and their moral validity.
1962
Rachel Carson publishes Silent Spring, an environmental science book that documented the environmental harm caused by pesticides. It is recognized as the environmental text that “changed the world.”

2005
Launched in November 2005 on the initiative of two European Commissioners (G. Verheugen and J. Potocnik) and a Member of the European Parliament (D. Roth-Behrendt), the European Partnership for Alternative Approaches to Animal Testing (EPAA) began operations in 2006.

2016
The terminology NAMs (New Approach Methodologies) is used for the first time in Helsinki. From then , all alternatives to animal testing will be referred as such - under the principles of 3Rs.

2022
European citizen initiative collecting more than 1 million signatures “SAVE CRUELTY FREE COSMETICS - COMMIT TO A EUROPE WITHOUT ANIMAL TESTING

1738
Digesting Duck - automaton in the form of a duck - is created by Jacques de Vaucanson

1975
Peter Singer publishes in 1975, Animal Liberation. This book was a philosophical bombshell. It forever changed the conversation about our treatment of animals.
2008
EUSAAT, the European Society for Alternatives to Animal Testing, is the European 3Rs Society and is actively promoting the protection of experimental animals according to the 3Rs-Principle. The society was founded in 1993 as MEGAT (Mitteleuropäische Gesellschaft für Alternativmethoden zu Tierversuchen) and changed its name to EUSAAT in 2008.

2019
To face the several daunting challenges of neurological research - organoids are sent into space to « grow a smarter model for brain ».

2021
In September 2021 the European Parliament adopted a resolution on plans and actions to accelerate the transition to innovation without the use of animals in research, regulatory testing and education.
